HCM Capital cultivates value through mutual sharing. Your substantial contribution unite us in envisioning of future Bitcoinization world. Subscribe and get the latest updates.
Disclaimer
1. This research report is for informational purposes only. The content of this report is for the purpose of learning, sharing, and communication, and should not be considered as investment or legal advice. Audiences should conduct thorough research on relevant investments to avoid deception.
2. The company reserves all intellectual property rights to all content. Therefore, direct usage without written authorization or consent from the company is prohibited.
3. The information contained in this report is based on sources believed to be reliable, but the company does not guarantee its accuracy or completeness. All opinions, estimates, and projections expressed in this report are subject to change without notice. If important data is used, audiences should verify it themselves.
4. Investing in Bitcoin, involves risks and investors should carefully consider their financial situation, investment objectives, risk tolerance, and seek advice from an independent financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Table of Contents
4. Dynamics in The Asian Market
5. Regulatory Forward Movements
7. Geopolitical Risks and Opportunity
1. Executive Summary
Bitcoin, as a decentralized digital asset, represents a groundbreaking innovation with the potential to reshape global finance. In Asia, Bitcoin's adoption and regulatory landscape vary significantly across countries, influenced by factors such as market dynamics, regulatory frameworks, and geopolitical tensions.
1.1 Economic and geopolitical tension shapes the market dynamic
The adoption of Bitcoin across Asia reflects a complex interplay of market dynamics, influenced by a multitude of factors. One significant aspect is the varied perspections towards Bitcoin, stemming from the diverse economic and cultural contexts prevalent throughout the region. While some countries have embraced Bitcoin as a means of financial inclusion and innovation, others have approached it with caution, citing concerns about regulatory oversight and potential risks.
Additionally, the adoption of Bitcoin is shaped by regulatory frameworks established by governments, which can either facilitate or hinder its use and development. Geopolitical tensions, particularly in regions like China, further impact Bitcoin's adoption by influencing government policies and attitudes towards cryptocurrencies. Moreover, economic uncertainties, such as fluctuating currency values and market instability, also play a role in shaping the adoption and perception of Bitcoin within the Asian market. The complex interaction of these market dynamics underscores the nuanced landscape of Bitcoin adoption and use cases across Asia.
1.2 China’s Bitcoin crackdown shifts the landscape
China has experienced three notable Bitcoin crackdowns. Initially, in 2013, the government prohibited banks and payment processors from dealing with cryptocurrencies. In 2017, significant platforms were closed down, and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) were banned due to apprehensions regarding fraud and financial stability. The most recent crackdown unfolded in 2021, with constraints placed on both mining and trading operations. Statista reports that Chinese bitcoin mining activity, which once accounted for 75% of the global total in 2019, plummeted to nearly 0% following the crackdown.
1.3 Hong Kong ranked as the top of most crypto-ready region
Initially pegged to the sterling pound, Hong Kong shifted to a peg with the U.S. dollar in 1972 after Britain abandoned its fixed exchange rate. This move, marking the end of the Sterling Area, left Hong Kong balancing political ties with China and financial reliance on the U.S. dollar. Despite maintaining currency stability, challenges such as increased borrowing costs and liquidity drain during U.S. interest rate hikes arose. Hong Kong emerged as the top "crypto-ready" region, showcasing readiness for Bitcoin amid concerns over CCP influence. Alongside the launch of the Bitcoin and Ether ETFs, mark a significant step in Hong Kong's financial landscape, which could potentially lead 25 billion of new demand, given the substantial presence of family offices in wealth management, this underscores the considerable potential for these financial instruments to cement Bitcoin as a mainstream asset class.
1.4 Growing institutional adoptions
In Asia, institutional adoption of Bitcoin is surging, reshaping the financial landscape. Factors like regulatory clarity, and recognition of digital assets as legitimate investments are driving this shift, especially in Central & Southern Asia. Countries like Japan and South Korea lead this adoption, benefiting from clear regulations that encourage market participation. Singapore is also seeing significant institutional interest, attracted by pro-business policies and supportive regulatory environments. Institutional interest mainly centers on accessing licensed custodians, establishing deep liquidity pools, and managing counterparty risk. The anticipated approval of Bitcoin spot ETFs is poised to further drive adoption, offering compelling trading opportunities and avenues for long-term investment.
1.5 Bitcoin usecase: treasury asset, global remittance and clearance
Bitcoin serves as a treasury asset for institutions and facilitates global remittances and clearance processes, offering efficiency and transparency. Institutions and corporations increasingly view Bitcoin as a compelling treasury asset due to its scarcity and decentralized nature, offering protection against currency devaluation and inflation. Recent investments by companies like Metaplanet and Boyaa Interactive International underscore growing institutional interest. Additionally, The Bitcoin Lightning Network addresses inefficiencies in global remittances, providing a faster, cheaper, and more transparent alternative to traditional channels, benefiting migrant workers in Asia. Its decentralized ledger further streamlines global clearance processes, reducing costs, enhancing security, and ensuring accurate and tamper-proof transaction records, promising increased financial inclusion, efficiency, and innovation as adoption continues to grow.
1.6 Geopolitical risks and opportunity
Bitcoin offers a decentralized financial system, providing individuals and entities with greater autonomy and security, particularly in regions with unstable governance. Its censorship-resistant nature allows users to circumvent government controls, promoting financial inclusion and empowerment, while its borderless design facilitates seamless cross-border transactions, enhancing global economic cooperation. Yet, its disruptive potential poses challenges to geopolitical stability and regulatory frameworks, with concerns over money laundering and market volatility prompting regulatory actions and market uncertainty. Geopolitical tensions can impact Bitcoin's adoption and value, necessitating responsible usage and education initiatives. Promoting understanding of Bitcoin technology, compliance with regulations, and responsible investment practices can mitigate risks and foster wider adoption, benefiting individuals and governments alike.
1.7 Bitcoin’s rise in Asia
In Asia, the ascent of Bitcoin has been nothing short of remarkable. With its decentralized nature and potential for high returns, Bitcoin has captivated investors and enthusiasts alike across the continent. The allure of Bitcoin as a hedge against economic instability and inflation has resonated particularly strongly in regions with volatile fiat currencies. Additionally, the advancement of the underlying innovation behind Bitcoin, has sparked interest and investment from governments and businesses, further fueling the growth of Bitcoin in Asia. As regulatory frameworks evolve and infrastructure for Bitcoin becomes more robust, Asia is poised to continue leading the global adoption of Bitcoin.
2. Introduction
Bitcoin represents one of the most groundbreaking innovations in modern world. As a decentralized digital currency, it has the potential to revolutionize the way the world approaches money and assets. Its creation marked a significant departure from traditional financial systems, offering an alternative that operates outside the control of governments and central banks. Bitcoin's underlying technology, ensures transparency, security, and immutability of transactions, thereby fostering trust in an otherwise trustless environment. Moreover, Bitcoin's finite supply and deflationary nature challenge the conventional notions of currency and store of value, prompting discussions on its role as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty.
As institutional interest in Bitcoin grows, with major companies and financial institutions incorporating it into their investment strategies, its influence on global economics and geopolitics becomes increasingly pronounced. Indeed, Bitcoin's emergence signifies a fundamental shift in the way we perceive and interact with money, paving the way for a more decentralized and inclusive financial ecosystem.
This report offers a comprehensive overview of the Bitcoin ecosystem in Asia, providing insights into key market dynamics and regulatory trends. It delves into various use cases emerging in the Asian market and explores the geopolitical opportunities and risks associated with Bitcoin adoption in the region.
3. Bitcoin in Asia Overview
Bitcoin's presence in Asia is marked by a complex interplay of market dynamics, regulatory frameworks, and geopolitical factors. Across the region, Bitcoin has seen both challenges and opportunities, shaping its adoption and use cases uniquely in each context. In Asia, a diverse range of economic and cultural contexts exists, leading to varied attitudes towards Bitcoin. While some countries have embraced Bitcoin as a means of financial inclusion and innovation, others have adopted a more cautious approach, citing concerns about regulatory oversight and potential risks. Geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainties in certain regions have further influenced the adoption and perception of Bitcoin.
3.1.1 China mainland
China's approach to Bitcoin has been characterized by strong regulatory restrictions. The government's stance towards Bitcoin has evolved over the years, reflecting its concerns about financial stability, capital outflows, and potential risks associated with Bitcoin or cryptocurrencies.
3.1.1.1 History of regulatory restrictions
In 2013, China's central bank, the People's Bank of China (PBOC), prohibited financial institutions from handling Bitcoin transactions, effectively banning banks and payment processors from dealing with cryptocurrencies. Nevertheless, the market remains active as many individuals perceive Bitcoin primarily as a vehicle for trading and seeking short-term gains, especially in its early years.
From less than 10% in Jan 2012, the yuan makes up nearly 100% of all Bitcoin trading on Jan 2017. Source: Deutsche Bank
In 2017, China intensified its crackdown on domestic cryptocurrency exchanges, shutting down several major platforms and banning ICOs, citing concerns about fraud, money laundering, and financial stability.
In 2019, China's National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) categorized Bitcoin mining as an "undesirable" industry in its initial list of sectors subject to encouragement, restriction, or phase-out by local governments. This classification was attributed to the energy-intensive nature of Bitcoin mining, which involves computationally verifying Bitcoin transactions to earn newly minted Bitcoin rewards. The NDRC's decision placed Bitcoin mining among the industries deemed highly polluting according to their assessment.
In 2021, the State Council reaffirmed previous crypto policies by advocating for the restriction of both crypto mining and trading activities. Prior to this, major Bitcoin mining hubs such as Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang, and Sichuan provinces had already initiated policies that hindered the operations of Bitcoin miners. Subsequent to the State Council's announcement, provincial governments took proactive measures to eliminate crypto mining altogether. Regulators pointed to Bitcoin's significant energy consumption and its potential threat to the country's environmental objectives as primary reasons for justifying the intensified crackdown. Similar to the repercussions of the 2017 crypto exchange crackdown, Bitcoin miners were compelled to either cease operations permanently or relocate to more crypto-friendly jurisdictions. Given that approximately 50% of the world's Bitcoin mining power was concentrated in China prior to the crackdown, the global Bitcoin economy inevitably bore the brunt of China's ban on Bitcoin mining.
China’s Bitcoin crackdown shifts the mining landscape. Source: Statista
When the nation with the largest share of Bitcoin hash rate initiated nationwide crackdowns on the industry, a significant number of miners were compelled to halt operations. Consequently, the total hash rate of the Bitcoin network plunged to 84.79 exahashes per second (EH/s) in early July then bounce back.
The Bitcoin network implied daily hash rate (7-day moving average), year-to-date. Source: Coin Metrics.
Chinese regulators proceeded to implement a comprehensive ban on crypto trading in September. Unlike previous measures targeting crypto transactions, this ban left no ambiguity regarding the country's stance on cryptocurrency, with the central bank, in collaboration with nine other state bodies including the police and the supreme court, issuing a joint statement that clarified the that all crypto transactions, including both crypto-to-fiat and crypto-to-crypto transactions, as well as trading and investments, have been deemed illegal, regardless of whether they are conducted through domestic or foreign platforms. This encompasses transactions involving major cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Tether. In addition, Chinese nationals engaged in marketing or technical support roles for foreign exchanges will now be subject to legal prosecution.
3.1.2 Hong Kong
As a global financial hub, Hong Kong has seen a vibrant Bitcoin ecosystem emerge alongside its traditional financial markets. While there are regulations in place, including licensing requirements for crypto exchanges, Hong Kong remains relatively open and see Bitcoin as part of its Web 3.0 development initiative. The city has a growing number of Bitcoin startups and a robust community of enthusiasts. However, political tensions and uncertainties surrounding the region's autonomy have introduced challenges, with some investors seeking Bitcoin as a hedge against geopolitical risks.
3.1.2.1 Vibrant community
Hong Kong hosts several exchanges and platforms that cater to both retail and institutional investors. These platforms offer various services, including spot trading, futures contracts, and derivatives. The city's active trading scene attracts investors from around the world, contributing to Hong Kong's status as a major player in the global market. Nevertheless, trading wasn't the primary purpose for which Bitcoin was designed to function. Bitcoin adoption is growing in Hong Kong, with an increasing number of merchants accepting Bitcoin payments. Additionally, Bitcoin ATMs are available across the city, providing convenient access for users to buy and sell Bitcoin using cash or other payment methods.
As one of the world's leading international financial centers, Hong Kong has long been committed to becoming a hub for global wealth and asset management. Family offices, as the highest form of wealth management, can leverage significant multiplier effects by channeling funds into Bitcoin. Deloitte's latest research report pointed out that by the end of 2023, Hong Kong had approximately 2,703 single-family offices. Consequently, envisioning Bitcoin's parallel growth alongside the flourishing family office sector suggests a potential surge in Bitcoin adoption within the region.
3.1.2.2 Permissive regulation
Hong Kong has relatively lenient regulations compared to mainland China, allowing for greater flexibility in Bitcoin-related activities. While the government regulates crypto exchanges under existing laws, there is no specific legislation governing Bitcoin itself. The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) provides guidelines for cryptocurrency platforms and fund management firms operating in Hong Kong, ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations.
3.1.2.3 The Hong Kong Dollar history and Bitcoin’s geopolitical impacts
The Hong Kong Dollar was initially pegged to the sterling pound. However, after the United States ceased the convertibility between gold and the U.S. dollar in October 1971, Britain abandoned its fixed exchange rate with the U.S. dollar. This change extended to the Sterling Area countries, effectively ending the Sterling Area in 1972. Subsequently, in the same year, the Hong Kong dollar was pegged to the U.S. dollar.
In some respects, this situation places Hong Kong in a delicate position between the political influence of the Chinese Communist Party and its financial dependence on the U.S. dollar and fiscal policies. Despite maintaining a stable currency, Hong Kong experienced a notable increase in borrowing costs following a significant market sell-off. As the U.S. initiated interest rate hikes, Hong Kong faced a substantial liquidity drain while striving to uphold its currency peg. While the peg to the U.S. dollar affords Hong Kong a degree of financial autonomy, the economy has been significantly impacted by a declining population, reduced demand, and increased borrowing costs to sustain the peg. Hong Kong also grappled with stringent COVID-19 restrictions, leading to rising unemployment rates that somewhat reflect trends observed in China.
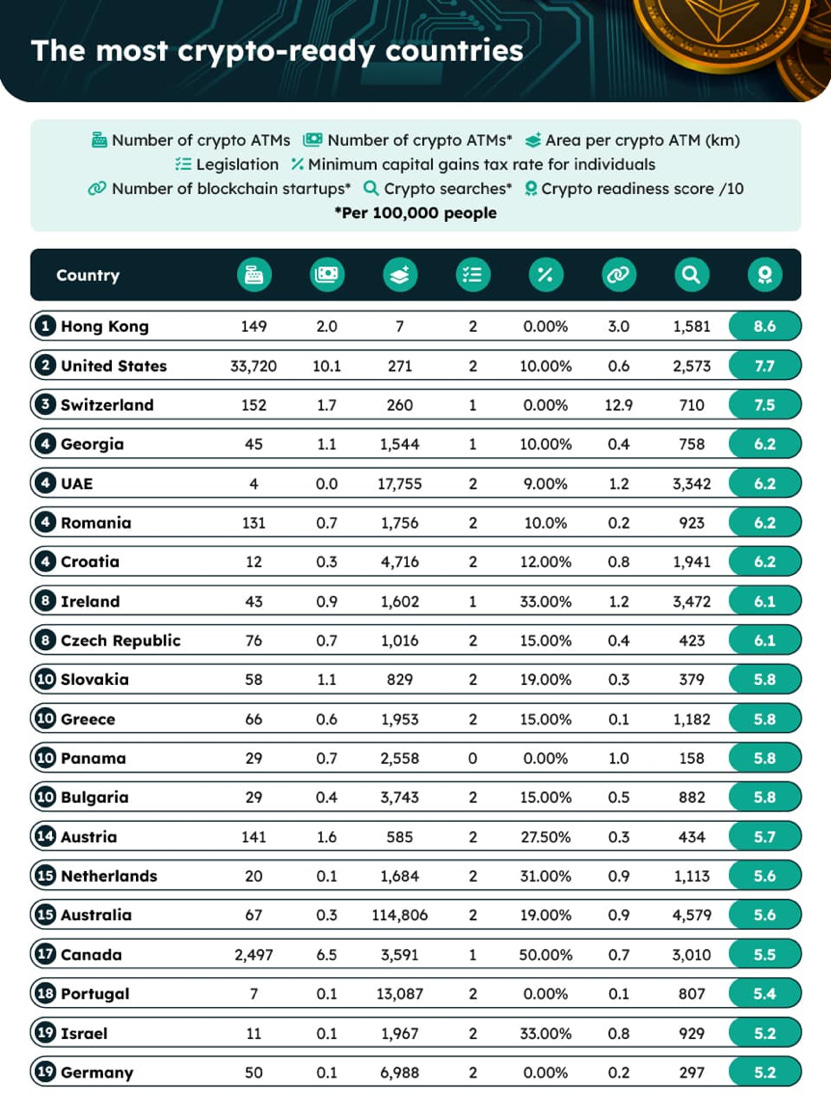
Given its tenuous financial and political circumstances, Hong Kong emerged as the top-ranking "crypto-ready" region. This designation was determined based on several key indicators, including the presence of crypto ATMs, favorable regulatory frameworks, a thriving startup ecosystem, and equitable tax policies etc—all of which signify a nation's readiness to embrace cryptocurrencies including Bitcoin. According to a study, Hong Kong achieved the highest crypto-readiness score of 8.6. Additionally, Hongkong previously experienced a surge in Bitcoin trading during the 2019 protests, underscoring the demand for a decentralized peer-to-peer exchange free from governmental influence, particularly given concerns about the erosion of autonomy by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) in Hong Kong.
The most crypto-ready countries. Source: Coincu
3.1.2.4 Hongkong Bitcoin Spot ETFs
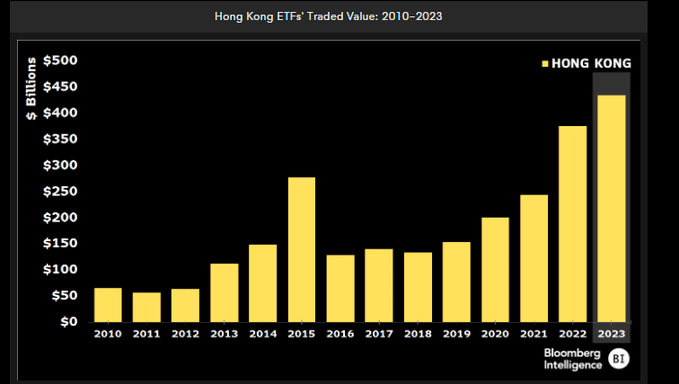
Asia’s inaugural exchange-traded funds (ETFs) directly investing in Bitcoin and Ether commenced trading in Hong Kong on April 30, 2024, this marks a notable stride in the city's endeavor to establish itself as a cryptocurrency hub. These ETFs were introduced by fund managers, including ChinaAMC, Harvest International, and Bosera Asset Management, collaborating with HashKey Capital, the investment wing of Hong Kong-based crypto firm HashKey Group. According to data from Wind, the three major asset management companies collectively manage 3.42 trillion yuan ($470 billion) in mutual funds and ETFs. The launch is expected to enhance Hong Kong's competitiveness as an international financial center. Following the approval of Bitcoin ETFs in the U.S. in January, Hong Kong is now following suit. Unlike the U.S., where only cash transactions are accepted, Hong Kong's securities watchdog has approved a trading mechanism allowing the purchase and redemption of ETFs using cryptocurrencies. This innovation could enable crypto holders to utilize their ETF shares as collateral for traditional financial assets without the need to convert their virtual currencies into cash for such transactions. This highlights Hong Kong's ambition not only to keep pace with global markets but also to take the lead in virtual asset innovation and regulation worldwide.
The launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs in Hong Kong holds substantial implications for AUM. Source: Bloomberg Intelligence
3.1.3 Taiwan
Taiwan has positioned itself as a friendly environment for Bitcoin development. The government has taken a proactive approach, fostering innovation in the sector through regulatory sandboxes and initiatives to attract talent and investment. Taiwan has seen the emergence of Bitcoin startups, research centers, and supportive communities. Despite these favorable conditions, the ecosystem tends to refer to itself as "blockchain" rather than "Bitcoin”, the regulatory clarity and compliance remain key considerations for businesses operating in the Taiwanese Bitcoin ecosystem.
In Bitcoin's nascent stages, Taiwanese lawmakers displayed less enthusiasm; however, recent years have seen a shift in their stance. In 2017, the chairman of Taiwan's Financial Supervisory Commission (FSC), expressed openness to the development of cryptocurrencies and distributed ledger technology. He emphasized that fostering distributed ledgers presents a substantial opportunity for innovation and economic expansion in Taiwan. In September 2023, the Financial Supervisory Commission released guidelines emphasizing customer protection, highlighting the need for industry-wide standards. By forming an industry association, crypto firms aim to develop self-supervisory rules aligned with these guidelines, fostering a safer and more transparent operating environment. In April 2024, Taiwan's Ministry of the Interior has granted approval for the formation of an industry association by the local cryptocurrency sector, signaling a notable stride towards regulating the industry.
Given the government's approval, the working group is now tasked with finalizing all necessary preparations to formally establish the crypto industry association by the end of June, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Comprising 22 prominent crypto firms, the working group has actively guided the sector towards self-regulation. The establishment of the industry association marks a significant milestone for Taiwan's cryptocurrency sector, which has largely operated within an unregulated framework thus far.
4. Dynamics in The Asian Market
Bitcoin dynamics in the Asian market are shaped by a multitude of factors reflecting the region's diverse economic, regulatory, and cultural environments. Asia stands as one of the most significant markets for Bitcoin globally, with countries playing pivotal roles. Asia witnesses a growing interest from institutional players, including banks, asset managers, and technology firms. Cultural attitudes towards finance, technology, and risk-taking also significantly influence Bitcoin dynamics in Asia, impacting consumer behavior and investment trends. Additionally, geopolitical factors such as economic uncertainty and currency depreciation in certain countries may further drive demand for Bitcoin as a hedge against traditional financial risks.
4.1 Institution adoption
In recent years, Asia has witnessed a notable uptick in institutional adoption of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, signaling a significant shift in the region's financial landscape. Several factors have contributed to this trend, including regulatory clarity, increasing interest, and growing acceptance of digital assets as legitimate investment vehicles.
Growing institutional adoption in Central & Southern Asia and Oceania (CSAO). Source: Chainanalysis
Countries like Japan and South Korea have been at the forefront of institutional adoption, with established regulatory frameworks providing a level of certainty for market participants. In Japan, for example, the recognition of Bitcoin as a legal form of payment has paved the way for the integration of Bitcoin into mainstream financial services, leading to the emergence of regulated exchanges and investment products tailored for institutional investors. Singapore, often regarded as a global financial hub, has also witnessed growing institutional participation in the Bitcoin market. The pro-business policies, supportive regulatory environment, and robust infrastructure have attracted institutional investors, asset managers, and companies looking to capitalize on the potential of digital assets. Similarly, South Korea has seen a surge in institutional interest in Bitcoin, driven by a combination of factors such as a young and tech-savvy population, and a favorable regulatory environment. The government's efforts to create a conducive environment for startups have further fueled institutional adoption in the country.
Institutional interest is primarily focused on three key areas: gaining access to licensed custodians, establishing deep pool liquidity, and effectively managing counterparty risk. From a product perspective, the Bitcoin spot ETF’s approval is anticipated to drive a surge in adoption, attracting significant investor interest. This could present compelling trading opportunities for large institutions and provide additional avenues for long-term investment. With allocators showing bullish sentiment, the arrival of these ETFs is expected to facilitate increased participation from both allocators and traders, leveraging market inefficiencies. The Hongkong Bitcoin and Ether Spot ETFs could potentially lead 25 billion of new demand, highlighting the substantial potential for these financial instruments to establish Bitcoin as a mainstream asset class.
4.2 Geopolitical factors
Geopolitical factors play a significant role in influencing the adoption of Bitcoin on both macro and micro levels. Geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainties can drive individuals and institutions to seek alternative financial assets, such as Bitcoin, as a hedge against currency devaluation and geopolitical risks. For example, in countries experiencing political instability or economic crises, citizens may turn to Bitcoin as a store of value and a means of preserving wealth amidst volatile local currencies. Moreover, Bitcoin's decentralized nature makes it resistant to government censorship and control, appealing to individuals living under authoritarian regimes or in countries with restrictive financial policies. In such environments, Bitcoin can serve as a tool for financial freedom and resistance against government overreach.
Half of the top 6 countries with positive YoY growth in crypto transaction volume located in Asia. Resource: Chainanalysis
Lower middle-income (LMI) countries have shown remarkably robust adoption rates, surpassing those of other income categories. The World Bank utilizes four classifications to categorize countries based on their income levels, determined by gross national income (GNI) per capita. LMI countries’ GNI per capital range from $1,086 – $4,255, and example countries including Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand.
Crypto adoption based on country income bracket. Resource: Chainanalysis
LMI countries often represent nations on the ascent, characterized by dynamic industries and growing populations. Many of these countries have experienced substantial economic development in recent decades, propelling them from the low-income bracket. Significantly, LMI countries are home to 40% of the world's population, surpassing any other income category. With this demographic weight, it becomes evident that Bitcoin is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of these nations. Moreover, the ongoing institutional adoption, primarily led by organizations indicates a robust momentum. This convergence of factors paints a promising outlook for the future. If current trends persist, we could witness a fusion of bottom-up and top-down Bitcoin adoption, catering to the diverse needs of individuals across both segments.
4.3 Ordinals and Bitcoin assets
Ordinal NFTs offer a method of creating Bitcoin NFTs by associating data, such as texts, images and videos, with individual satoshis on the base Bitcoin mainnet. Unlike their predecessors, Ordinal NFTs do not exist on a separate layer from Bitcoin. Additionally, the BRC-20 token standard represents an experimental approach to minting and transferring fungible tokens on the Bitcoin mainnet, while the Runes protocol provides a token standard for issuing fungible tokens on Bitcoin, aiming to offer users a more efficient means of creating such tokens. However, these methods contribute to congestion on the Bitcoin mainnet and drive up transaction fees. Despite some use cases, such as Microstrategy Orange, which utilizes Ordinals to integrate digital signatures into emails, enhancing sender identity verification for recipients, the congestion remains a serious issue for the Bitcoin network.
Ordinals lead to higher transaction fee. Source: Dune
Nevertheless, this type of Bitcoin layer 2 has gained popularity in Asian countries. Consequently, certain tokens and projects within the Bitcoin ecosystem have seen increased interest from traders anticipating a potential BTC rally. These investments provide traders with a means to indirectly capitalize on Bitcoin's anticipated increase in value, without resorting to futures products or leveraging strategies. Currently, it's unclear where this trend, which has gained significant momentum, will ultimately lead. A vast majority, approximately 95%, of the entire ecosystem comprises trivial memcoins, often hyped by the Chinese community and primarily fueled by speculation.
According to a post on Binance Square, Mac (@MacnBTC), a cryptocurrency influencer on X, remarked, "One of my close friends from China sent me this video. It shows 70+ year old grandmothers in China learning how to buy and trade BRC20. This explains why Binance has already listed two BRC20 assets, and I believe they will continue to do so. Ordinal tokens are generating immense hype in China." Clearly, ordinal tokens are utilized as a means to exploit older individuals into investing money, often resulting in losses. The manner in which people hype ordinal tokens closely resembles that of other crypto issuers. It all hinges on the narrative, which often diverges from Bitcoin's original ethos and value propositions.
5. Regulatory Forward Movements
As each country develops its own rules and regulations, engaging with each on their terms becomes a complex operation. Financial regulators are increasingly prioritizing the protection of retail investors and the safety, stability, and efficiency of financial services across both fiat and Bitcoin realms. Unlike fiat markets, where regulators seek a balance between protection and intervention versus free market dynamics, navigating the Bitcoin landscape requires an additional layer of practical and pragmatic regulation due to its anonymous and decentralized nature. In traditional finance, transactions are seldom anonymized, and central bodies such as banks and exchanges can swiftly intervene. However, the Bitcoin industry presents regulators with a novel challenge. With transactions frequently anonymized and decentralized, regulators must adapt their approaches to effectively oversee this evolving landscape while maintaining market integrity and investor protection.
Possible policy options for regulating crypto-assets. Source: Hong Kong Monetary Authority
In Hong Kong, authorities are actively positioning their country as a leader in Web3.0. This rare alignment among regulators, governmental officials, and industry leaders signifies a unique opportunity. Notably, regulators have begun permitting licensed exchanges to offer retail trading services, propelling the city into prominence. Additionally, there's openness to approving spot Bitcoin ETFs, indicating a serious commitment to leveraging the digital asset industry for economic growth. The world is keenly observing Hong Kong's progress. With the region poised to become a significant crypto hub, its success could influence mainland China's stance on Bitcoin. Even a modest shift in China's approach could have substantial implications for the digital asset sector, given ongoing investment in the country. Meanwhile, Singapore maintains a pragmatic approach to digital assets, attracting investment and talent. Similarly, other major Asian economies like Japan and South Korea are crafting regulations tailored to foster investor confidence and growth. Despite regulatory uncertainties, India sees active engagement, underscoring the global interest and potential of digital assets
Regulatory rules in Southeast Asia. Source: Saison Thinking
6. Bitcoin Usecase in Asia
Bitcoin's usecase in Asia as a treasury asset, a solution for global remittances, and a facilitator of global clearance processes highlight its transformative potential in reshaping traditional financial systems and empowering individuals and institutions across the region. As adoption continues to grow, Bitcoin is poised to play an increasingly vital role in driving financial inclusion, efficiency, and innovation in Asia and beyond.
6.1 Treasury asset
Firstly, Bitcoin has emerged as a compelling treasury asset for institutions and corporations across Asia. Recognized for its scarcity and decentralized nature, Bitcoin offers a hedge against currency devaluation and inflation, particularly in regions prone to economic uncertainty. Institutions view Bitcoin as a store of value, akin to digital gold, providing portfolio diversification and long-term wealth preservation. Moreover, Bitcoin's borderless nature and accessibility make it an attractive option for treasury management, enabling seamless cross-border transactions and reducing reliance on traditional banking infrastructure.
Metaplanet, a publicly-listed Japanese company offering hotel-related and other services, has disclosed its acquisition of ¥1 billion (approximately $6.25 million) worth of Bitcoin. After the announcement on April 2024, Metaplanet's stock price experienced a notable surge, signaling investor confidence in the company's decision to allocate funds to Bitcoin. Boyaa Interactive International, a publicly traded Hong Kong holding company specializing in online card and board games, seeks shareholder approval to allocate $45 million to invest in Bitcoin on December 2023. HongKong publicly-listed company Meitu Inc has hold $60 million worth of Bitcoin. These instances underscore the growing institutional interest and expanding Bitcoin market.
6.2 Global remittance and clearance
Bitcoin serves as a powerful solution for global remittances, addressing inefficiencies and high costs associated with traditional remittance channels. In many Asian countries, migrant workers send significant portions of their earnings back to their home countries to support their families. Bitcoin Lightning Network offers a faster, cheaper, and more transparent alternative to traditional remittance services, enabling individuals to send funds directly to recipients with minimal fees and delays. Furthermore, Bitcoin's decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of fraud and corruption often associated with traditional remittance systems.
Over 70% of cross-border banking customers in the surveyed markets send money internationally. Source: RFI Global
Transaction costs still well above UN target. Source: FXC Intelligence analysis, World Bank
Additionally, Bitcoin facilitates global clearance processes by providing a decentralized and immutable ledger for recording transactions. Traditional clearance systems often involve multiple intermediaries, complex procedures, and lengthy settlement times. Bitcoin offers a more efficient and transparent alternative, enabling parties to transact directly with each other in a peer-to-peer manner, without the need for intermediaries. This not only reduces costs and processing times but also enhances security and reliability, ensuring that transactions are recorded accurately and cannot be tampered with.
7. Geopolitical Risks and Opportunity
Bitcoin offers an alternative financial system that operates independently of traditional government-controlled currencies. This decentralization grants individuals and entities greater financial autonomy and security, especially in regions with unstable or authoritarian regimes. Bitcoin's censorship-resistant nature enables users to bypass capital controls and sanctions imposed by governments, facilitating financial inclusion and empowerment for marginalized populations. Additionally, Bitcoin's borderless nature enables frictionless cross-border transactions, fostering economic cooperation and trade on a global scale.
However, Bitcoin's disruptive potential also poses risks to geopolitical stability and traditional financial systems. As Bitcoin adoption grows, governments may perceive it as a threat to their monetary sovereignty and regulatory control. Concerns about money laundering, terrorist financing, and tax evasion associated with Bitcoin have prompted regulatory crackdowns and bans in some countries, leading to increased regulatory scrutiny and uncertainty in the market. Moreover, Bitcoin's volatility and speculative nature can destabilize financial markets and exacerbate economic volatility, posing systemic risks to global financial stability.
Geopolitical tensions and conflicts can influence Bitcoin's price and adoption. Heightened geopolitical risks, such as trade disputes, sanctions, and geopolitical unrest, can drive demand for Bitcoin as a safe-haven asset, similar to gold. Conversely, regulatory actions and geopolitical crackdowns on Bitcoin can dampen investor sentiment and hinder its adoption in certain regions.
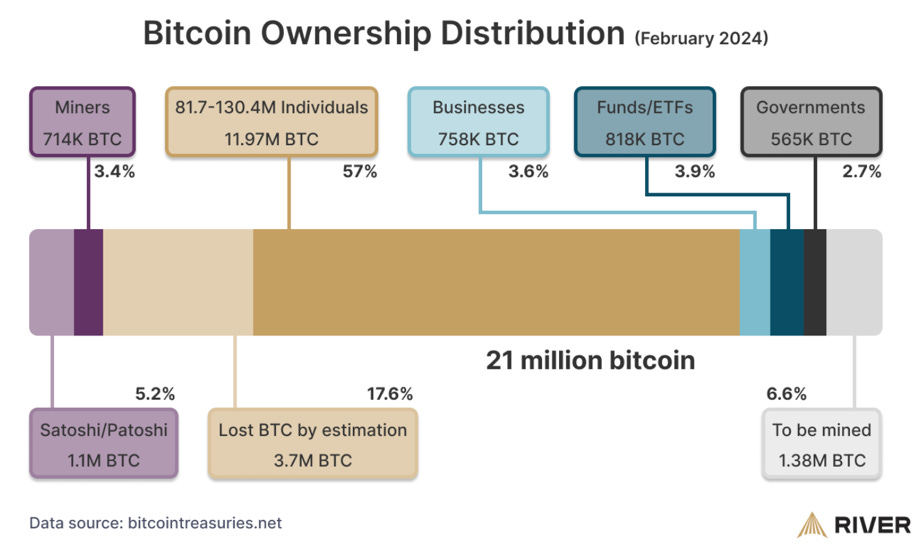
Based on data from River, 57% of Bitcoin is owned by individuals. This underscores the importance of responsible Bitcoin usage among the general populace. Encouraging individuals to embrace Bitcoin education and promoting its correct usage can play a pivotal role in mitigating risks and fostering wider adoption, ultimately benefiting both individuals and governments alike.
Individuals takes up 57% of Bitcoin ownership. Source: River
Effective Bitcoin education initiatives can empower individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the Bitcoin landscape responsibly. This includes understanding the fundamentals of Bitcoin technology, learning best practices for securely storing and managing digital assets, and grasping the implications of Bitcoin's decentralized nature on personal financial sovereignty. Moreover, promoting the correct usage of Bitcoin entails advocating for compliance with regulatory requirements and ethical guidelines. By adhering to anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations, individuals can contribute to building a more transparent and trustworthy ecosystem. Similarly, promoting responsible investment practices, such as conducting thorough due diligence before investing in Bitcoin-related projects or platforms, can help mitigate the risks of fraud and financial loss. Furthermore, individuals can actively engage in efforts to promote Bitcoin adoption by advocating for its integration into mainstream financial systems and encouraging businesses to accept Bitcoin payments. By demonstrating the utility and value of Bitcoin as a viable alternative to traditional currencies, individuals can contribute to expanding its use cases and increasing its acceptance in everyday transactions.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, Bitcoin stands as a transformative force in the modern financial landscape, offering a decentralized alternative to traditional currencies and assets. Across Asia, Bitcoin's impact is profound, with diverse use cases ranging from treasury assets for institutions to solutions for global remittances and clearance processes. As institutional interest in Bitcoin grows, regulatory frameworks are evolving to balance innovation and investor protection, shaping the future of Bitcoin adoption in the region.
The dynamics of Bitcoin adoption in Asia are influenced by a myriad of factors, including regulatory clarity, geopolitical tensions, and cultural attitudes towards finance and technology. While Bitcoin presents opportunities for financial inclusion and empowerment, it also poses risks to geopolitical stability and traditional financial systems. However, with responsible usage and education, individuals can navigate the Bitcoin landscape effectively, contributing to wider adoption and fostering a more transparent and trustworthy ecosystem.
As Asia continues to embrace Bitcoin, it is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future, driving innovation, and empowering individuals and institutions across the region.
9. Reference
1. https://www.statista.com/chart/25969/Bitcoin-mining-hashrate-share-of-computer-energy-by-country/
4. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-10/08/content_5641404.htm
5. https://coincu.com/112200-hong-kong-the-most-crypto-ready-country/
9. https://aibc.world/news/taiwan-gives-go-signal-for-the-creation-of-crypto-sector-association/
10. https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/2023-global-crypto-adoption-index/
11. https://www.desfran.com/crypto-valley-of-asia-the-next-big-thing/
12. https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/central-southern-asia-cryptocurrency-adoption/
13. https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/spot-Bitcoin-etfs-commence-trading-in-hong-kong
14. https://techcrunch.com/2023/09/12/institutional-crypto-adoption-asia/
15. https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/africa-cryptocurrency-adoption/
16. https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/2023-global-crypto-adoption-index/
17. https://sovryn.com/all-things-sovryn/Bitcoin-runes-tokens
18. https://chain.link/education-hub/ordinals-Bitcoin-nfts
20. https://www.binance.com/en/square/post/1548215393178
21. https://www.businessinsider.com/Bitcoin-trading-china-yuan-remnibi-2017-1
22. https://dune.com/dgtl_assets/Bitcoin-ordinals-analysis
24. https://Bitcoinmagazine.com/business/asias-microstrategy-metaplanet-buys-1-billion-Bitcoin-yen
26. https://www.coingecko.com/en/public-companies-Bitcoin
27. https://www.stcn.com/article/detail/1151343.html
29. https://rfi.global/the-global-remittance-market-surges-to-almost-800-billion-in-2022/
Copyright @2024, HCM International Company. All rights reserved.